Quickstart Tutorial: Sending Your First Transactional Email via API (in 5 Minutes)
Quickstart Tutorial: Sending Your First Transactional Email via API (in 5 Minutes)
Introduction: Welcome to the Fluxomail quickstart guide! Fluxomail is an AI-powered, developer-first email platform optimized for speed and reliable inbox delivery1. It provides a simple HTTP+JSON API to send emails and track deliverability events in real-time, giving developers a fast way to integrate email without sacrificing reliability2. In this tutorial, we'll walk through how to send your first transactional email via the Fluxomail API in under five minutes. (Transactional emails are one-off emails triggered by user actions - think welcome messages or password resets.) If you're searching for a send email API tutorial or wondering how to send email with an API using Node.js or Python, you're in the right place. We'll cover step-by-step instructions for both Node.js and Python, highlight Fluxomail's quick onboarding benefits, and point you to next steps like domain authentication for better deliverability.
Prerequisites: Fluxomail Account & API Key Setup
Before coding, make sure you have the following:
Fluxomail Account: Sign up and log in to the Fluxomail dashboard (free tier is available for testing).
API Key: Generate an API key from your dashboard. Go to Settings → API and click "Create API key." Copy the key and keep it secure (preferably as an environment variable)3. Fluxomail provides instant API keys on demand - no waiting or complex setup. This key will be used to authenticate your API calls.
Fluxomail's platform uses API keys for authentication, so you can get started immediately after signing up. There's no additional setup required beyond grabbing your key. 🚀
Sending an Email via API with Node.js (Step-by-Step)
Fluxomail's API is language-agnostic, but let's start with Node.js. If you're wondering how to send an email with an API in Node.js, it only takes a few lines of code. We'll use Node's native fetch() to make an HTTP POST request to Fluxomail's send endpoint.
Install Requirements: In a Node.js project (Node 18+ recommended for built-in fetch), ensure you have your environment ready. No special SDK is needed - the call is a standard HTTPS request. Use an environment variable for the API key (e.g. process.env.FLUXOMAIL_API_KEY) for security.
Prepare the Request: Fluxomail's send API endpoint is POST https://api.fluxomail.com/api/v1/emails/send. You'll need to include your API key in the header and the email details (recipient, subject, content) in JSON format. For safety, we also include an Idempotency-Key header with a unique value - this ensures if you retry the request (e.g. due to a network hiccup), Fluxomail won't send duplicates but will return the original result4.
Node.js Example - Sending a Transactional Email:
import crypto from 'crypto'
const API_KEY = process.env.FLUXOMAIL_API_KEY // your Fluxomail API key
const BASE_URL = 'https://api.fluxomail.com'
const res = await fetch(`${BASE_URL}/api/v1/emails/send`, {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
Authorization: `Bearer ${API_KEY}`,
'Idempotency-Key': `send-${crypto.randomUUID()}`, // unique key for this request
},
body: JSON.stringify({
to: 'user@example.com',
subject: 'Hello from Fluxomail',
content: 'Hi there, this is a test email via Fluxomail API.',
htmlContent:
'<p>Hi there, this is a <strong>test email</strong> via Fluxomail API.</p>',
}),
})
const data = await res.json()
console.log('Response:', data)
In this snippet, we call the Fluxomail API using fetch. We provide the recipient's email (to), a subject line, and both text (content) and HTML (htmlContent) bodies for the email. The Authorization header carries our API key (as a Bearer token), and we generate a random UUID for Idempotency-Key to avoid duplicate sends on retries. On success, Fluxomail will return a JSON response with details about the send. For example, you should receive a response containing a unique sendId along with a status (e.g. "sent") and a messageId5:
{
"sendId": "sends_12345abcdef",
"status": "sent",
"messageId": "0000000000000001-...-000000",
"reused": false
}
What does this mean? Essentially, Fluxomail has queued/sent your email successfully. The sendId is an identifier you can use to query the status or timeline of that email later, and status: "sent" indicates it was accepted for delivery. If you were to accidentally repeat the request with the same Idempotency-Key, you'd get reused: true and the same sendId back - Fluxomail intelligently prevents sending the same email twice4.
- Verify Delivery (Optional): With Fluxomail, you can retrieve a delivery timeline for the email using the sendId. For a quick check, you might log in to the Fluxomail dashboard to see the send in your live timeline. Alternatively, you can call the
GET /api/v1/sends/{sendId}endpoint to fetch events. In this quickstart, we won't dive deep into that, but know that events like delivered, bounced, opened, and clicked are automatically tracked and tied to your sendId in real-time6 - no additional configuration needed.
Sending an Email via API with Python (Step-by-Step)
Next, let's do the same thing in Python. This will show how to send an email with an API in Python using Fluxomail. We will use the popular requests library to make the HTTP call.
Install Requirements: Make sure you have requests installed (pip install requests). As before, have your Fluxomail API key ready (we'll use an environment variable for it in the code).
Prepare the Request: The endpoint and payload are the same. We will include the API key in the Authorization header and use Python's uuid module to generate an idempotency key. Then we send the JSON payload with the email details.
Python Example - Sending a Transactional Email:
import os
import uuid
import requests
API_KEY = os.environ.get('FLUXOMAIL_API_KEY') # your Fluxomail API key
BASE_URL = "https://api.fluxomail.com"
payload = {
"to": "user@example.com",
"subject": "Hello from Fluxomail",
"content": "Hi there, this is a test email via Fluxomail API.",
"htmlContent": "<p>Hi there, this is a <strong>test email</strong> via Fluxomail API.</p>",
}
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {API_KEY}",
"Idempotency-Key": f"send-{uuid.uuid4()}",
}
response = requests.post(f"{BASE_URL}/api/v1/emails/send", json=payload, headers=headers)
print("Status:", response.status_code)
print("Response:", response.json())
In this Python code, we construct the request similarly to the Node.js example. The requests.post call sends the email. If everything is set up correctly, the status code should be 200 (OK) and the JSON response (printed out) will include the sendId and status just like in the Node example.
Note: The use of an Idempotency-Key (with a random UUID) is optional but highly recommended. It allows you to safely retry the request if needed -- Fluxomail will return the same result without sending the email twice4. This is one of the no-bloat defaults Fluxomail provides to make your life easier. In fact, Fluxomail is built to handle deliverability details automatically: it auto-generates unsubscribe links, tracks opens/clicks, and handles bounces/complaints for you by default76. That means you can focus on sending emails, while Fluxomail handles compliance and tracking behind the scenes (no custom code or "glue" webhooks needed for basic deliverability events).
Quick Onboarding Benefits
As shown above, sending an email via the Fluxomail API is straightforward. To recap, here are a few reasons why Fluxomail makes this process so quick and developer-friendly:
Instant API Keys: You can generate API credentials with one click and start sending immediately3 - no lengthy provisioning or approval process.
Copy-Paste Integration: The API calls are simple HTTP requests. The example code is essentially copy-and-paste ready, with no complex SDK setup required. Fluxomail's API uses sensible defaults and minimal parameters to get you going fast.
No-Bloat Defaults: Important features are enabled by default. For instance, open and click tracking are automatically injected into your HTML emails8, and a one-click unsubscribe header is added by default to comply with email best practices7. You don't need to manually handle these in your code.
Built-in Deliverability Guardrails: Fluxomail is a deliverability-first platform. It ensures authenticated sending and compliance out-of-the-box (SPF/DKIM, proper headers, suppression lists, etc.), so your emails have a high chance of landing in the inbox by default910. In short, "More inbox, fewer incidents." 🙌
By combining instant setup, a clean API, and managed deliverability features, Fluxomail lets developers integrate email into their apps in minutes while trusting that the emails will reach users reliably.
Next Step: Authenticate Your Domain for Better Deliverability
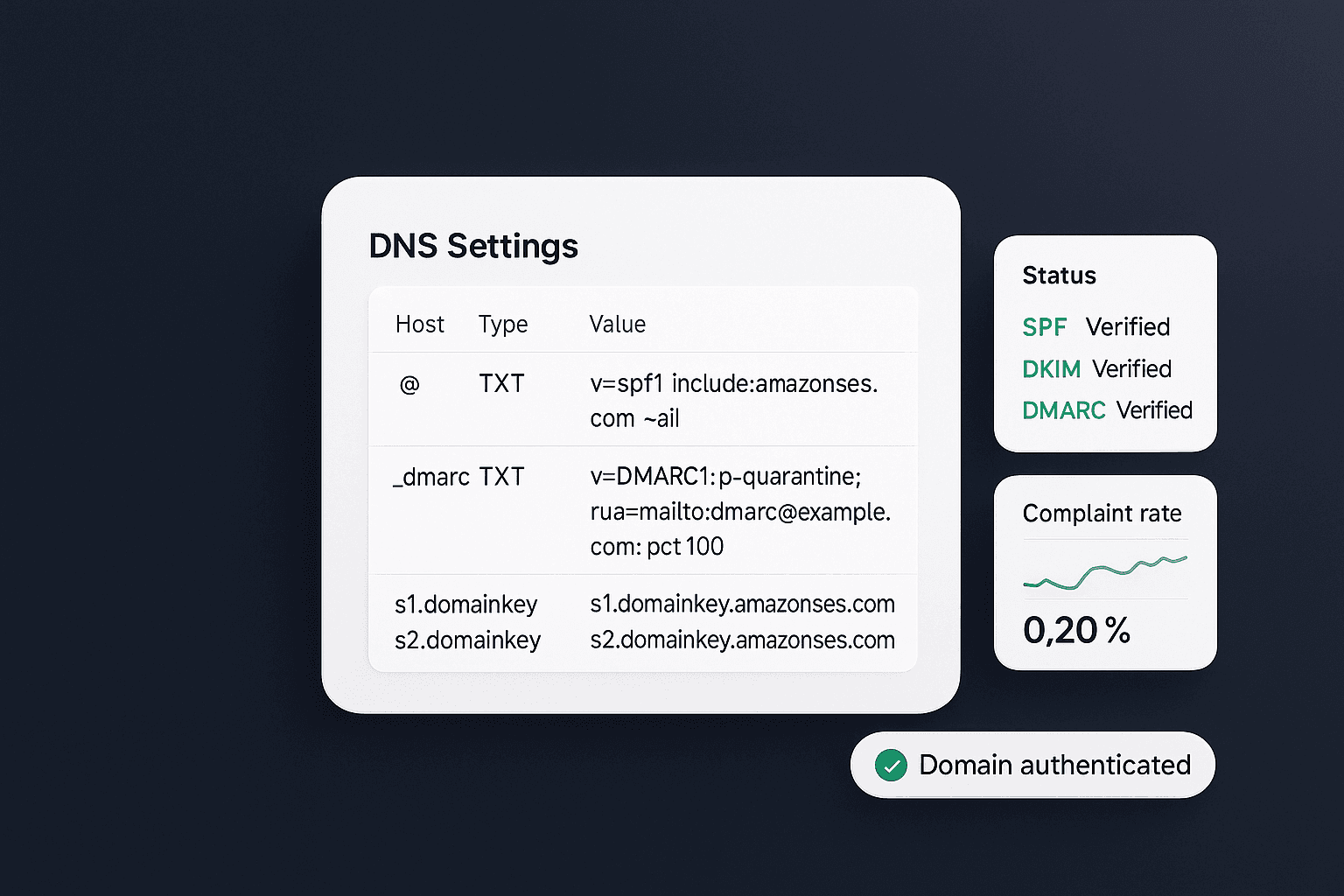
After sending your test email, the next important step is to authenticate your sending domain. Domain authentication (setting up SPF and DKIM, and optionally DMARC) is critical for building sender reputation and ensuring inbox delivery. In Fluxomail, this process is streamlined with a wizard in the dashboard.
How to Authenticate Your Domain:
Add Your Domain: In the Fluxomail dashboard, navigate to Deliverability (or a similarly named section) and choose "Add Domain." Enter the domain you'll send from (e.g. yourdomain.com) and specify a desired From address like no-reply@yourdomain.com11.
Configure DNS Records: Fluxomail will provide you with DNS records to add for verification - typically an SPF record and one or more DKIM records, and a suggested DMARC policy. These might look like TXT records that need to be added in your domain's DNS settings. Follow the on-screen instructions or use the provided SPF/DKIM setup wizard to get the exact values. Add the records to your domain's DNS, then go back to Fluxomail and click "Verify" or "Re-check" until the status indicates that SPF/DKIM have passed12.
Done - Domain Verified: Once Fluxomail confirms the records, your domain is authenticated. All emails you send via the API will now come from your domain with proper cryptographic signatures, which mailbox providers love to see. This boosts your deliverability and credibility (no more "via fluxomail.com" appearing on your emails).
Fluxomail's documentation has a detailed domain authentication guide if you need more help. The platform essentially guides you through SPF/DKIM setup and verifies everything automatically912, so this step is usually quick. With a verified domain, you'll also unlock detailed delivery signals - for example, you can monitor if Gmail or other ISPs are successfully delivering your messages without issues.
Tip: After authenticating, try sending another test email via the API. You should see that the email's headers show your domain's DKIM signature and SPF passes, indicating a fully authenticated send. This will greatly improve the chances of your email landing in the inbox rather than spam.
Conclusion: Monitor & Extend Your Email Integration
Congratulations - you've sent your first transactional email via the Fluxomail API! 🎉 From here, you can build on this foundation. Fluxomail provides a robust toolset for developers to monitor and enhance their email sending:
Delivery Logs & Live Timeline: Every email send in Fluxomail comes with a live timeline of events. You can use the Fluxomail dashboard's Developer Console / Logs to search for your send and see events like Delivered, Opened, Clicked, Bounced in real time1314. This "single pane of glass" view is incredibly useful for debugging - it's like having an x-ray into your email's journey. If an email didn't reach a user, the timeline will show whether it bounced or was deferred, etc. (For an API approach, you can also use the
GET /api/v1/sends/{sendId}endpoint to retrieve the same information programmatically.)Webhooks for Real-Time Events: For deeper integration, Fluxomail allows you to set up webhooks so your application can receive real-time notifications of email events. You can configure webhooks to POST events (deliveries, bounces, opens, clicks, complaints) to your own endpoints. This way, your system can automatically react (e.g. mark a user's email as bounced in your database) as soon as it happens. Check out Fluxomail's webhooks documentation for how to configure endpoints and verify signatures for security.
Further Documentation and Tools: Fluxomail's docs cover many more features and best practices. For example, you might want to read about setting up category preferences (to manage unsubscribe groups), exploring the engagement timeline UI in the dashboard, or using policy keys to apply sending rules (e.g. distinguishing transactional vs. marketing sends). There are also guides on using webhooks, tracking, and analytics to get the most out of the platform. If you're interested in deeper debugging tips, see our guide on viewing email logs and troubleshooting delivery (which goes into using the unified logs and event webhooks for debugging). And if you plan to send high volume, Fluxomail's rate limit handling and idempotent design will have you covered (remember to reuse the same Idempotency-Key on retries to avoid dupes4!).
In summary, Fluxomail makes it extremely easy for developers to get started with sending emails via API. With quick setup, friendly SDK-like HTTP calls, and built-in deliverability features, you've accomplished in minutes what might take much longer on other platforms. As you continue, be sure to leverage Fluxomail's resources:
📖 Documentation: Refer to the official docs for any advanced usage. Key areas to explore next include the Domain Authentication guide (if you haven't set up SPF/DKIM yet), the sending logs and timeline sections for monitoring, and the Webhooks guide for receiving event data in your app.
🔗 Dashboard & Console: Use the Fluxomail dashboard's tools (like the Engagement Timeline and search) to observe your email sends. This developer-grade observability will help you quickly fix issues and optimize your integration14.
🤖 Feedback & Support: Fluxomail is built for developers, so if you run into any questions, don't hesitate to reach out to support or consult the community forums. The platform even includes an AI assistant and plenty of in-app tips to help you along15.
We hope this email API quickstart guide has demonstrated how easy it is to send a transactional email with Fluxomail via Node.js or Python. With your domain authenticated and your first email out the door, you're well on your way to integrating reliable email functionality into your application. Happy coding, and may all your emails land in the inbox! 📬🚀
Sources
- [1] FluxoMail
- [2] Introduction - Fluxomail Documentation
- [3] Quickstart - Fluxomail Documentation
- [4] FluxoMail
- [5] Send email - Fluxomail Documentation
- [6] Set up deliverability - Fluxomail Documentation
- [7] FluxoMail
- [8] Set up deliverability - Fluxomail Documentation
- [9] FluxoMail
- [10] FluxoMail
- [11] Set up deliverability - Fluxomail Documentation
- [12] Set up deliverability - Fluxomail Documentation
- [13] FluxoMail
- [14] FluxoMail
- [15] FluxoMail
- [16] Quickstart - Fluxomail Documentation
- [17] Send email - Fluxomail Documentation